What is Business Intelligence?
How is Business Intelligence used in Enterprises?
Key Functions of Business Intelligence
Types of Enterprise BI Users
Advantages of Business Intelligence
Challenges in implementing Business Intelligence
Factors influencing the success of BI in an organization
How are Business Intelligence systems implemented?
Business intelligence (BI) is the collection of strategies and tools used to analyze business information. It allows businesses to act quickly on internal and external data trends and data-driven decisions on time.
Companies use BI to enhance their decision-making processes, minimize operating costs and identify new areas of opportunity. It can be both a strategic and competitive advantage.
BI is not a new concept. In fact, BI tools have been around for more than a decade. There has been a recent spike in interest around BI due to the significant amount of data that is available to businesses today.
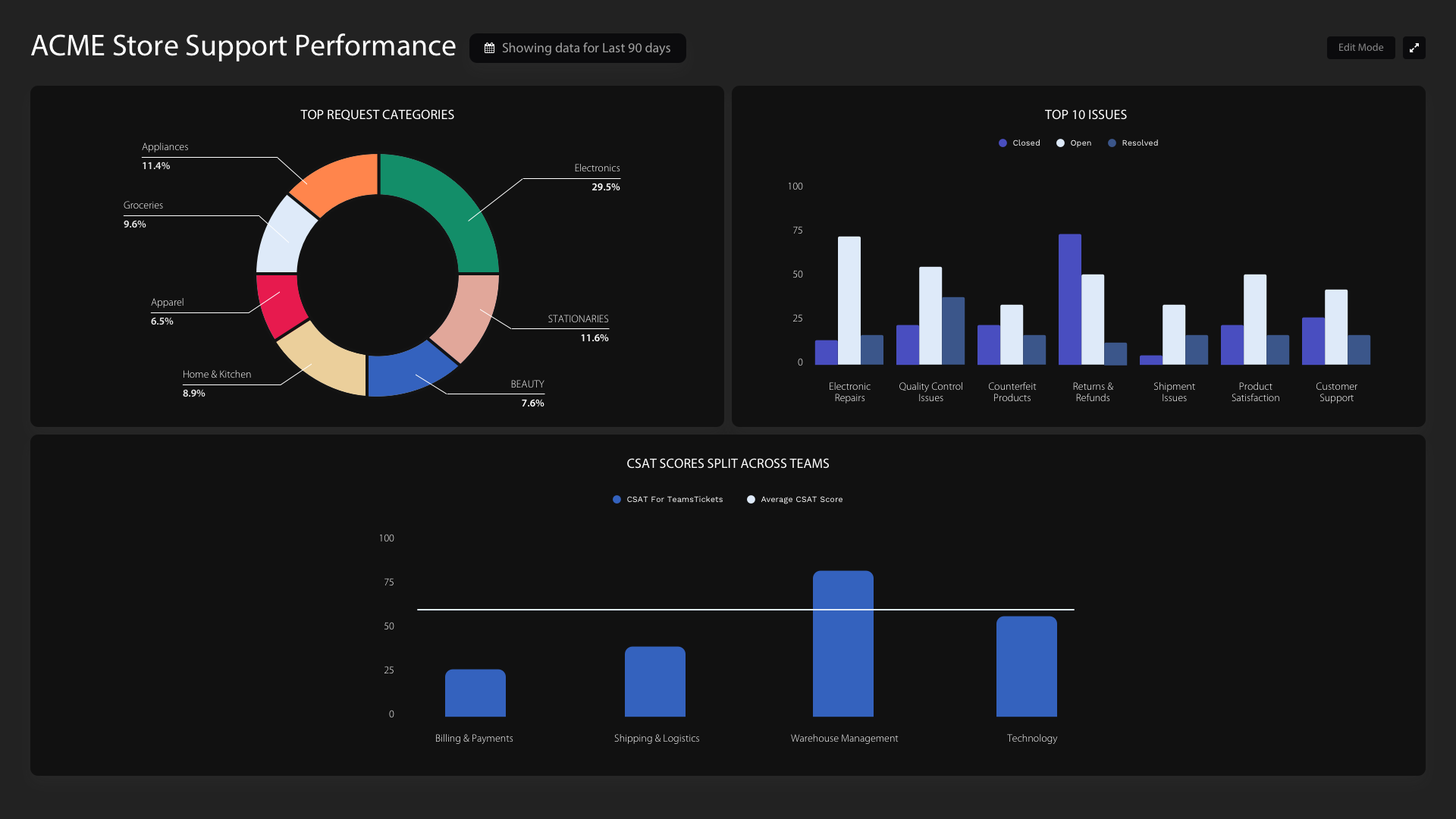
Measurement: BI tools are commonly used in measurement applications. Many business intelligence tools can take input data from sensors, CRM systems, ticketing systems, web traffic, and more to measure KPIs.
Analytics: To measure is only the beginning. The use of business intelligence software for analytics allows businesses to deeply understand their data, identify trends and insights, and drive business value with data-driven decisions.
Reporting: When enterprises start measuring KPIs and identifying trends, the need for a scalable data visualization and reporting framework increases. BI products can seamlessly generate reports for various business stakeholders, automate critical tasks for analysts, and replace the need for spreadsheets and word-processing programs.
Collaboration: Collaboration features allow users to work across the same data and same files together in real-time. Cross-device collaboration in BI platforms can be important when creating new reports or dashboards.
Enterprise Reporting: One of the key functions of business intelligence is enterprise reporting. Reports can take many forms and are produced using several methods. However, BI software can automate the report generation process. BI tools can bring enterprise-level scalability in report production and enable collaboration between the various stakeholder.
Business Analytics: Business Analytics is the process of examining data and figuring out patterns or trends to make key business decisions. Analytics can be descriptive, prescriptive, or predictive.
Descriptive analytics describes a dataset through measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and spread (range, standard deviation, etc.).
Prescriptive analytics is a subset of BI that prescribes specific actions to optimize outcomes. It is situation-dependent and it helps to determine a prudent course of action based on data.
Predictive analytics, also known as predictive modeling, is the use of statistical techniques to create models that can predict future or unknown events. It is used to forecast trends within a business, industry, at a macro level.
Data Mining: Data mining is the process of uncovering patterns in large datasets and it often incorporates machine learning (ML), statistics, and database systems to discover these patterns. Data mining is a key process in the pre-processing of data as it ensures a clean and proper data structure.
Benchmarking: Benchmarking is the use of industry-recognized KPIs to measure the success of a business, a project, or a business process. It is a very important activity in the BI ecosystem and widely used to make incremental improvements to a business.
The following are the key users of a Business Intelligence system in an Enterprise setting.
Data Analysts: Data analysts are statisticians who work with large volumes of data with the need to drill deep into it. BI system helps them to extract new insights from the data and to develop unique business strategies for the organization.
Business Users: These can be found from across the organization. Their needs can vary from working with complex data sets to using dashboards to keep track of the health of the business.
Company Leadership: These are the VP or C-suite members whose main responsibility is to lead the company effectively and to find ways to increase the profit of their business by improving operational efficiency in their business.
IT Users: The IT user also plays a primary role in setting up and maintaining the BI infrastructure.
Here are some of the advantages of using a Business Intelligence System:
BI systems boost productivity. With a BI program, It is possible for businesses to create reports and dashboards easily without spending a lot of time and resources. It helps the business make use of the abundance of data with relative simplicity.
BI improves visibility. BI helps to improve the visibility of business processes and make it possible to identify any areas which need attention.
BI systems fix accountability. BI system assigns accountability in organizations. There must be someone who should own accountability and ownership for business performance.
BI streamlines business processes. BI systems take out all complexity associated with business processes. It automates analytics by offering predictive analysis, computer modeling, benchmarking and other methodologies.
BI allows for data-driven decision making. BI system also helps organizations as decision-makers get an overall bird's eye view through typical BI features like dashboards and scorecards. It even non-technical users to collect and process data quickly. This allows putting the power of analytics in the hands of many thus allowing data-driven decision making across the organization.
Lack of Structured Data: Business Intelligence software requires data to be adequately structured to enable analysis and search-ability. This structuring can be done by adding context with metadata. Organizations that have unstructured or incomplete data will struggle to get buy-in from the stakeholders who cannot trust the reports.
Lack of Adoption: Many BI tools attempt to entirely replace older processes and workflows, and this often results in poor internal adoption, with users reverting to the tools and processes they’re familiar and comfortable with. BI implementations can fail because of the time it takes to create or run reports, which makes users less likely to adopt new technologies and more likely to revert to legacy tools.
Lack of User Training: Inadequate user or IT training is a major reason for business intelligence project failure. Inadequate training can lead to confusion and frustration on the user’s part leading to the project’s failure.
Lack of Stakeholder Communication: Internal communication is another key factor that can spell failure for business intelligence projects. Lack of communication between end-users and IT departments can detract from project success. Requirements from IT and purchasers should align with the needs of the team of end-users. If they don’t collaborate, the final product may not align with expectations and needs, which can cause frustration from all parties and a failed project. Successful projects provide business users with valuable tools that also meet internal IT requirements.
Lack of Proper Planning: The research and advisory firm, Gartner, warns against one-stop shopping for business intelligence products. Business intelligence products are highly differentiated, and it’s important that customers find the product that suits their organization’s needs for capabilities and pricing. Gartner suggests forming a dedicated team to work on a BI strategy with members pulled from these other departments.
Business intelligence implementation in an organization can only succeed if the organization is committed and executes it effectively. The critical factors that influence the success of a BI implementation include:
Business Sponsorship: Business sponsorship is the most important success factor because even the best BI implementation cannot overcome a lack of commitment from the business leadership. If there is a lack of budget or motivation with the executives, BI cannot be implemented to its full potential.
Business Needs and Requirements: It’s critical to understand the business needs to properly implement business intelligence software. This understanding extends to both the end-users’ needs and the IT departments’ needs, and often they may differ. To estimate the BI requirements, organizations must analyze all the needs of its various stakeholders.
Amount and Quality of the Data: A BI initiative can only be successful if it incorporates high-quality data at scale. Common data sources include customer relationship management (CRM) software, marketing platforms, customer support software, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) tools. Poor quality data will lead to poor decisions. By using data profiling techniques, the data is examined and statistics are collected for improved data governance. This helps in maintaining consistency, reduce risk, and optimizing search through metadata.
Data Gathering and Cleansing: Data may be gathered from many sources and this can easily overwhelm an organization’s decision-making capabilities. To prevent this and to create value with the BI software, organizations must identify their critical data sources. Business intelligence data often includes CRM data, competitor data, industry data, and more.
User Experience: Intuitive user experience is critical when it comes to business intelligence in order to promote user adoption and to drive more value from the BI tools. End-user adoption will be hard without simple and usable interfaces.
User Training: User Training drives end-user adoption. If the end-users of the BI software aren’t properly trained, adoption and value creation become much slower and difficult to achieve.
Monitoring and Improving: BI tools can end up becoming a black-box to many users, so it’s important to continually validate their outputs. Setting up a feedback system for requesting and implementing user-requested changes is important for driving continuous improvement in business intelligence.
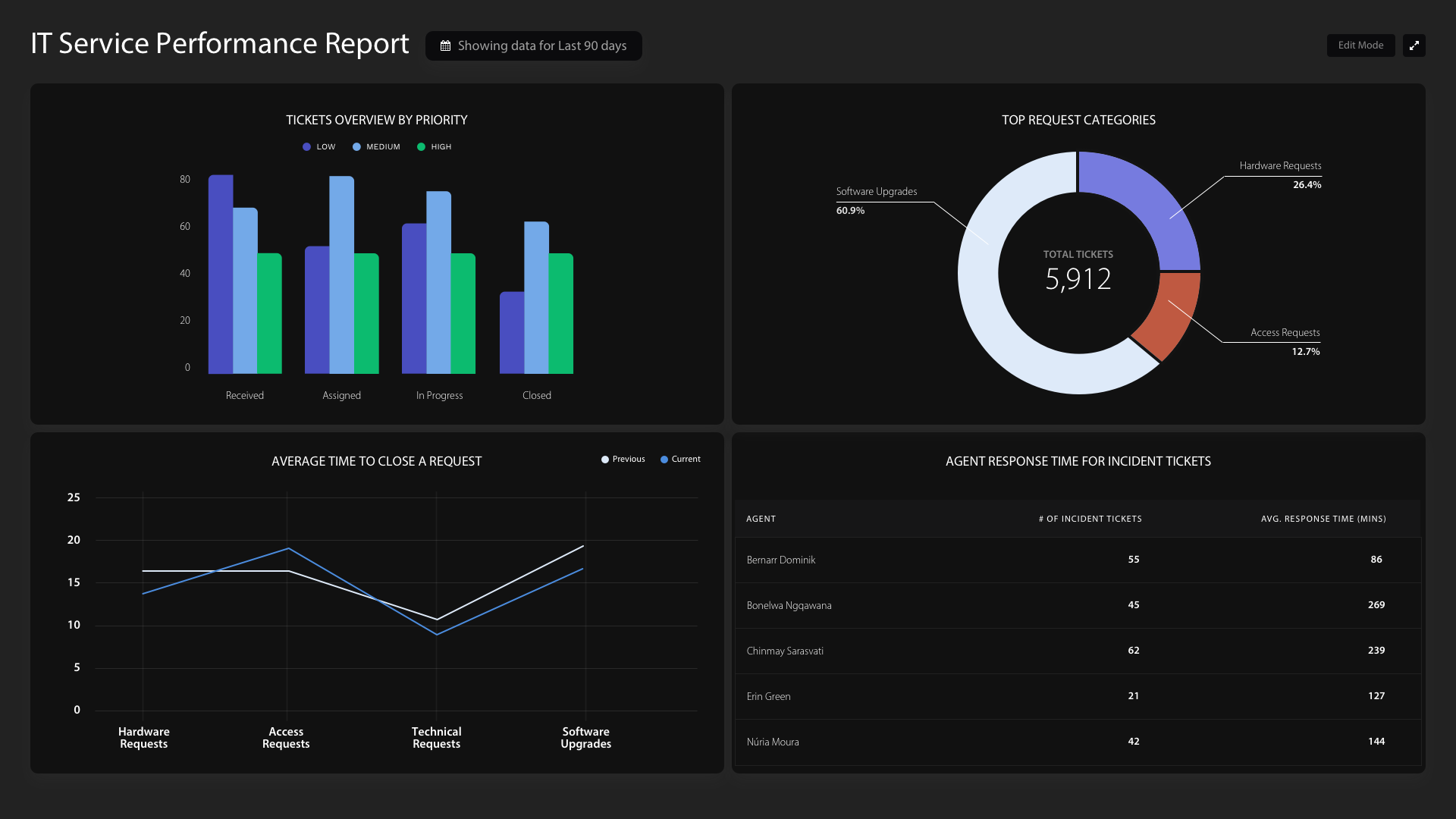
Once you have determined and ensured that all key success factors are in place then it is time to actually implement BI in your organization.
Ensure you have clean data, as discussed in the above section.
Define your goals clearly at the onset of the BI implementation. Specifically detail your expectations, every quarter or mid-way through the year and check if this is happening.
Train your staff well.
Do not spend too much time optimizing the reports. As the business evolves so does the data and thus the reports. Settle on reports that provide the most value with the least effort and then adjust them. Iterate and improve with time.
Business Intelligence is much more than a support for decision-making. If used correctly, BI has the potential to transform organizations.
Make sure to bookmark this guide to revisit when you begin the process of implementing BI for your organization.
HappyFox BI helps you gather data that is specific to your business needs and improve customer support with new insights. You can create your own drill-downs to plunge into help desk data, customize the visualizations and share it with the people who can make a difference. It syncs automatically with your HappyFox Help Desk account and pulls your latest customer support data. Integration with Zendesk and other key products coming soon.
We will help you build dashboards to gather key insights that your help desk is not providing. Book a demo today to learn more about HappyFox BI.
Talk to someone smart, quickly.